SUMMARY
Sealing is one of the most important factors for mobile hydraulics. This article will show you the principles, applications, benefits, and common failures of hydraulic seals
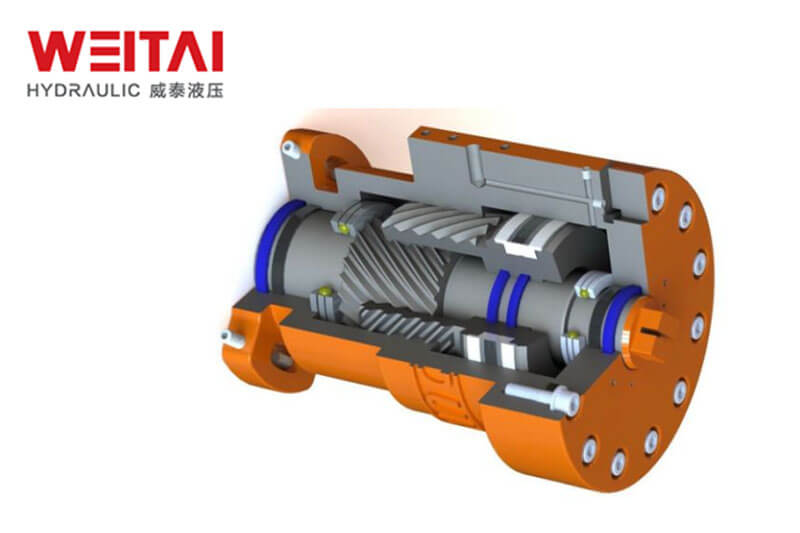

Principle of Hydraulic Seals
What are Hydraulic Seals?
Hydraulic seals are a form of gasket-like rings that are used to fill gaps between hydraulic cylinder components. Many different components are found in hydraulic cylinders, some of which get in contact with the fluid. Hydraulic seals are used to prevent fluid from seeping around these components. Hydraulic seals are made to suit the components of a hydraulic cylinder while providing a leak-proof seal.
The Construction of Hydraulic Seals
In the construction of hydraulic seals, the manufacturing process and the materials to be used in the manufacturing should be considered.
1) Manufacturing Process
During the manufacturing process, the hydraulic seals are made on a Computerized Numerical Control (CNC) lathe machine. They can be programmed with both standard and custom seal profiles. The CNC lathe works to cut the seal's shapes from the specified material using the profile's digitized data.
2) Hydraulic Seal Materials
Hydraulic seals come in a wide range of materials. Hydraulic seals are commonly made of rubber. Rubber hydraulic seals are malleable, long-lasting, and crack-resistant. Polyurethane hydraulic seals are also available and are the most common material used in hydraulic seals. Many of the features of polyurethane hydraulic seals are similar to those of rubber seals, however, they are generally more durable and resistant to wear.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a type of hydraulic seal that isn't as well-known as rubber or polyurethane (PTFE). PTFE is a flexible, durable, and temperature-resistant synthetic polymer. Specific operating parameters or constraints imposed by fluid type, pressure, fluid chemical compatibility, or temperature determine the material type.
Considerations When Choosing a Seal
The various considerations when choosing a seal include:
1) Shaft Speed
The maximum shaft speed is determined by the shaft finish, runout, housing bore, shaft concentricity, the kind of fluid being sealed, and oil seal material.
2) Temperature Range
The temperature range of the mechanism in which the seal is installed must not be higher than the seal elastomer's temperature range.
3) Seals and Pressure
Most conventional oil seals are only intended to resist extremely low pressures (about 8 psi or less). If there is or will be increased internal pressure, pressure relief is required.
4) Shaft Hardness
Shafts with a Rockwell (RC) hardness of 30 or higher might expect a longer seal life. The hardness should be increased to RC 60 when subjected to abrasive pollution.
5) Shaft Surface Finish
The best sealing results come from having the best shaft surface treatments. The spiral lead and the direction of the finish tool marks have an impact on the sealing efficiency. Polished or ground shafts with concentric (no spiral lead) finish marks produce the best sealing results. If spiral finish leads are required, they should point toward the fluid as the shaft rotates.
6) Concentricity of Seals
Seal life is reduced when the bore and shaft centers are misaligned because the wear is localized on one side of the sealing lip.
7) Shaft and Bore Tolerances
When shaft and bore tolerances are near, the best seal performance is attained. Shaft eccentricity, end play, and vibration are some of the other issues to consider.
8) Amount of Runout
The amount of runout must be maintained to a bare minimum. Bearing wobbling or shaft whip are the most common causes of the center of rotation movement. This difficulty is exacerbated when it is combined with misalignment. Flexible couplings, contrary to popular assumption and usual practice, cannot adjust or compensate for misalignment.
9) Seal Lubricants
When seals are regularly lubricated with oil that has a suitable viscosity for the application and is compatible with the seal lip elastomer material, they perform significantly better and last much longer. The possibility of seal incompatibility, especially with specific additives and synthetic lubricants, should not be overlooked.
Applications, Benefits, and Common Failures of Hydraulic Seals
Applications of Hydraulic Seals
Power transmission
Oil refineries
Off-highway
Manufacturing
Automotive
Benefits of Hydraulic Seals
Hydraulic seals prevent dirt from entering any internal part of a mechanical system.
It can have a design that allows it to work in low and high-pressure system operations. It means a lot to high-power-density hydraulic rotary actuators.
Hydraulic seals prevent any leakage, thereby reducing any chances of repair or downtime.
Hydraulic seals are affordable and require simple maintenance.
They are also highly adaptable and durable.
Hydraulic seals are capable of resisting wear and tear as well as water and chemicals.
Hydraulic seals are capable of reducing blowouts on oil plants to a greater extent.
A hydraulic seal can be changed within a short time (a few minutes).
They are designed to offer long services.
Common Failures of Hydraulic Seals
The common failures of hydraulic seals include:
1) Hydraulic Seal Hardening
When exposed to high temperatures, hydraulic seals become hard. The cause of this is either high-speed heat generation from stroking operations or high fluid operating temperatures. When seals harden, they lose their elasticity and crack, leading to the failure of the seal.
2) Seal Wear
Considerable damage can be caused on a seal by wear on the dynamic face of a seal lip due to excessive lateral load or insufficient lubrication.
3) Scarring in the Seal
The operating life of seals is dependent on the installation tools and processes. If there is an improper installation, cuts or dents may be caused in the dynamic lip of the seal. This will affect the hydraulic seal efficiency and introduce foreign elements into the hydraulic fluid.
4) Seal Fracture
Fracturing is a condition that results in breaking, bents, long cracks, and a complete breaking off of the seal’s dynamic side. This is because of excessive backpressure, high-pressure shocks, or low-grade materials when the seal is made.
5) Improper Installation
As already mentioned, improper installation may create problems with hydraulic seals. The result of it may be uncleanliness, contamination, unsafe handling, and incorrect sizing of the chosen seal. The design must be done correctly before the building of the seal to ensure proper sealing.
6) Contamination in Hydraulic Seals
When external flotsam and jetsam are introduced into the hydraulic rod, this causes contamination. When particles like mud, dirt, powder, or other tiny elements attach to the piston, they cause the seal to become dirty. If the seal is dirty, its ability to hermetically prevent contaminants from the area of the piston is lost.
7) Chemical Erosion
When the seal material encounters a corrosive fluid, it will break down. This occurs when the improper seal material is selected for an application. The chemical attack by hydrolysis, oil additives, and/or oxidation-reduction of seal elements can occur when there is a use of non-compatible materials. This results in the loss of the interface of the seal lip, swelling, softening of the seal durometer, and/or shrinkage of the seal. Discoloration of the seal is a sign of chemical erosion.
Conclusion
Hydraulic seals serve to prevent the leakage of fluid from within a system to the outside. There are different types of hydraulic seals, each offering its unique properties. When opting for a hydraulic seal, do carefully consider seals that perfectly suit a particular application. The considerations that can be investigated before selecting any seals must be but are not limited to fluid pressure range, temperature range, stroke speed, fluid type, hardware dimensions, and cylinder application.
In WEITAI GROUP, there are 10 hydraulic products delivered to clients per hour with zero leakage accidents. As one of the top hydraulic rotary actuator manufacturers, we provide hydraulic rotary drives of 90 degrees/180 degrees/220 degrees/360-degree rotation to adapt to different equipment applications. And the small and high torque rotary actuator from 300Nm to 38000Nm is suitable for various requirements of loading.
WEITAI GROUP is on the right track to becoming the leader of the hydraulic industry. With its advanced technology and the innovative design of its products, such as the Rotary Hydraulic Cylinder. WEITAI GROUP has established itself as a reliable and trustworthy brand. With its commitment to quality and its ability to provide customers with the best possible products, WEITAI GROUP is sure to be the leading brand of hydraulic products in the future. As the leading provider of hydraulic products, WEITAI GROUP will continue to strive to meet the needs of customers and remain the top choice for mobile hydraulic solutions in the market.
WEITAI Marketing Department
