There are three types of hydraulic actuators in the hydraulic industry. What are they? Where can they be applied to? In this blog, Weitai will introduce to you the three types of hydraulic actuators and their specific applications. Here is the index of this blog you can follow, or you can click to jump to the section you want to learn.
- Common Features of Hydraulic Actuators
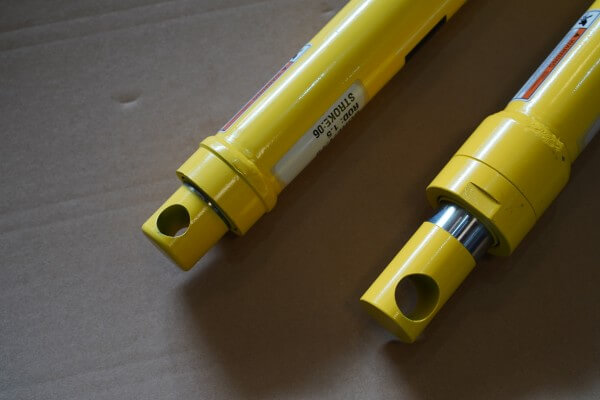
- Linear Hydraulic Actuators
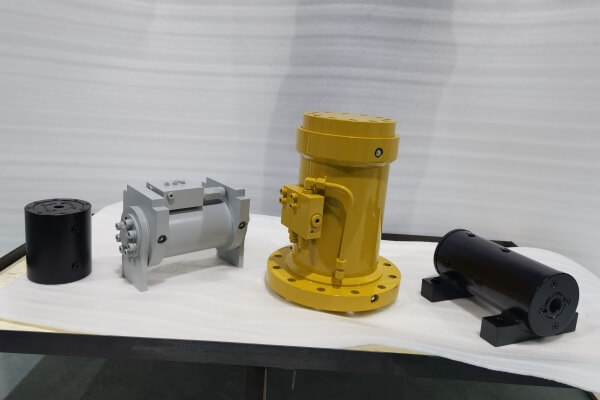
- Rotary Hydraulic Actuators
- Telescopic Hydraulic Actuators
Now, let’s dive into this blog.
Common Features of Hydraulic Actuators
There are some common features that all three types of hydraulic actuators. While there are some specific features for each of them.
High Torque Output: Rotary hydraulic actuators are capable of generating significant torque output, making them suitable for tasks that require the rotation of heavy loads or components.
Precise Positioning: Like linear hydraulic actuators, rotary hydraulic actuators offer precise control over motion, allowing for accurate positioning of rotary components. This precision is essential in applications where precise angular positioning or control is required.
Adjustable Speed and Torque: The speed and torque of rotary hydraulic actuators can be adjusted by controlling the flow rate of hydraulic fluid into and out of the actuator. This adjustability enables operators to tailor the actuator’s performance to match the requirements of different tasks or processes.
Compact Design: Rotary hydraulic actuators typically have a compact design, allowing them to be installed in tight spaces or integrated into existing machinery and equipment with ease.
Durability and Reliability: Rotary hydraulic actuators are designed to withstand harsh operating conditions and heavy-duty use. They are often constructed from durable materials and equipped with robust sealing mechanisms to prevent leakage and ensure reliable performance over time.
Integration with Control Systems: Rotary hydraulic actuators can be easily integrated into hydraulic control systems using valves, pumps, and other hydraulic components. This integration enables precise control over the actuator’s motion and facilitates automation in industrial processes.
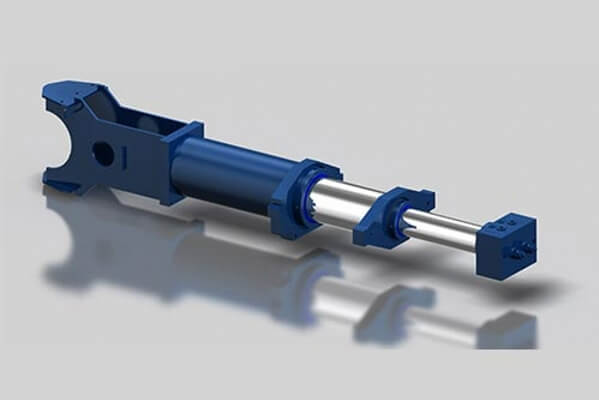
Linear Hydraulic Actuators
Definition
A linear actuator is a mechanical device that converts rotational motion into linear motion. It typically consists of a motor, a lead screw, a nut, and a housing that guides the linear motion. When the motor rotates, it drives the lead screw to move in or out of the nut, resulting in linear motion along the axis of the actuator.
Specific Feature
Linear Motion: The primary feature of a linear hydraulic actuator is its ability to convert hydraulic pressure into linear motion. This linear motion is typically used for tasks such as lifting, pushing, or pulling heavy loads along a straight path.
Applications
Automation: Linear actuators are used in automated machinery and systems to precisely control the position of components or tools.
Robotics: They are essential components in robotic systems for controlling the movement of robot arms, grippers, and other parts.
Medical devices: Linear actuators are used in medical equipment such as hospital beds, patient lifts, and surgical robots to provide precise and controlled movement.
Furniture: Electric linear actuators are used in adjustable furniture such as height-adjustable desks, recliners, and bed frames.
Aerospace: Linear actuators are used in aircraft and spacecraft for various applications, including landing gear deployment, flap control, and antenna positioning.
Industrial machinery: They are used in conveyor systems, packaging machines, and other industrial equipment for precise linear movement.
Home automation: Linear actuators can be used in smart home applications for opening and closing windows, doors, and blinds.
Rotary Hydraulic Actuators
Definition
A rotary actuator is a mechanical device that converts fluid, electric, or pneumatic energy into rotary motion. It typically consists of a motor, gears, and a shaft that rotates to perform work or control movements in a circular motion.
Specific Features
Rotary Motion: The primary function of rotary hydraulic actuators is to convert hydraulic pressure into rotational motion. This allows them to control the position or movement of rotary components in a wide range of industrial applications.
Bi-Directional Rotation: Depending on the design, rotary hydraulic actuators can provide rotation in either a single direction or both directions. This allows for flexibility in controlling the direction of rotation based on the specific requirements of the application.
Applications
Robotic arms: Rotary actuators are used in robotic systems to provide rotational movement for joints and end effectors.
Valve control: In industrial applications, rotary actuators are used to control valves for regulating the flow of liquids or gases in pipelines.
Material handling: They are used in conveyor systems and sorting machines to rotate or position objects during the manufacturing or packaging process.
Automotive industry: Rotary actuators are used in automotive applications for controlling functions such as opening and closing doors, adjusting mirrors, and operating convertible tops.
Aerospace: They are used in aircraft and spacecraft for various applications, including controlling flight surfaces, landing gear, and cargo doors.
Construction equipment: Rotary actuators are used in heavy machinery such as cranes, excavators, and loaders to provide controlled rotational movement.
Medical devices: They are used in medical equipment for tasks such as adjusting the position of imaging devices or surgical tools.
Entertainment industry: Rotary actuators are used in stage lighting, camera movement, and special effects in theaters, concerts, and film production.
Telescopic Hydraulic Actuators
Definition
A telescopic actuator, also known as a telescoping actuator or telescopic cylinder, is a type of linear actuator that consists of multiple nested sections that extend and retract to provide a longer travel range compared to traditional linear actuators. As each section slides out from the previous one, the actuator effectively “telescopes” to achieve a greater overall length.
Specific Features
Telescoping Design: The defining feature of telescopic hydraulic actuators is their telescoping design, which allows multiple stages or sections of the actuator to collapse into each other when retracted and extend to their full length when extended. This design enables the actuator to achieve long stroke lengths while maintaining a compact overall length.
Long Stroke Length: Telescopic hydraulic actuators are capable of providing long stroke lengths relative to their retracted length. This feature makes them ideal for applications where a large range of motion is required within a limited space, such as in dump trucks, cranes, and other heavy machinery.
Variable Length Configurations: Telescopic hydraulic actuators often offer the flexibility to configure the number of stages or sections based on the specific requirements of the application. This variability allows for customization of the actuator to accommodate different stroke lengths and load capacities.
Applications
Dump trucks: Telescopic actuators are used to lift and tilt the dump bed of trucks for unloading materials such as sand, gravel, and debris.
Fire trucks: They are used in aerial ladder trucks and platforms to extend and retract the ladder or platform for firefighting and rescue operations.
Material handling equipment: Telescopic actuators are used in cranes, forklifts, and other lifting equipment to extend and retract booms or arms for reaching high or distant objects.
Mobile machinery: They are used in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial vehicles for functions such as extending and retracting outriggers, stabilizers, or platforms.
Recreational vehicles: Telescopic actuators are used in RV slide-out rooms to extend living spaces for increased comfort and convenience.
Marine applications: They are used in boats and yachts for deploying and retracting swim platforms, gangways, and other marine equipment.
Aerospace: Telescopic actuators are used in aircraft and spacecraft for applications such as extending and retracting landing gear, antennas, and cargo doors.
Automotive industry: They are used in car carriers and tow trucks for extending and retracting ramps or platforms for loading and unloading vehicles.
Conclusion
These hydraulic actuators play an important role in various types of mechanical equipment. They have the advantages of compact structure, small size, lightweight, small inertia, and stable operation, and can meet various complex motion needs.